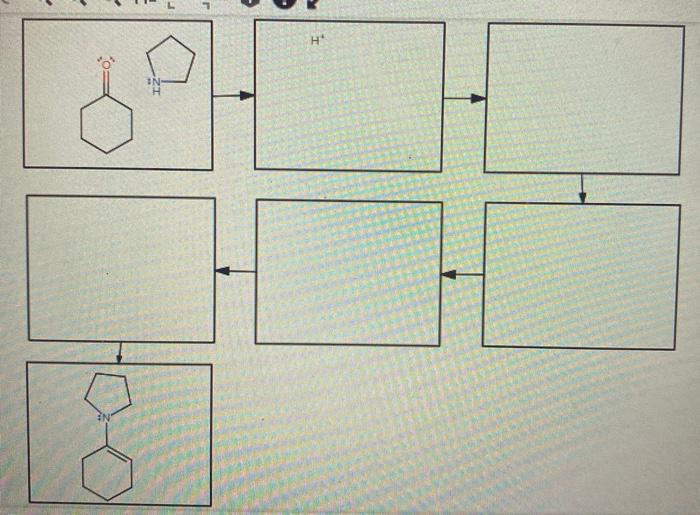
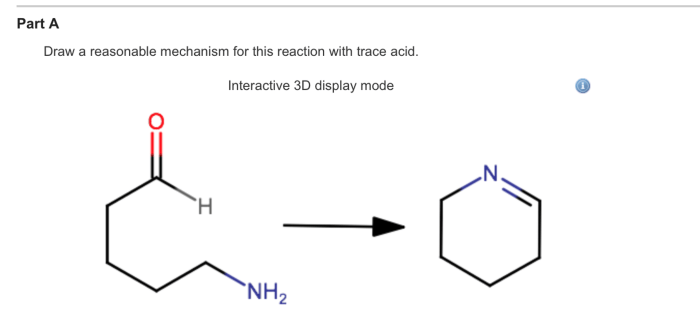
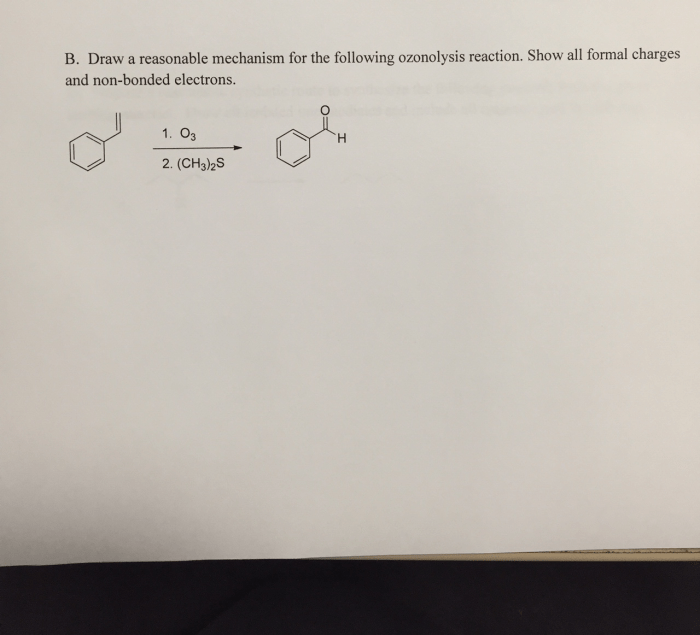Delving into the realm of draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:, this comprehensive guide embarks on an enlightening journey, unveiling the intricacies of reaction mechanisms with gaya akademik dan tone otoritatif. Embarking on this exploration, we will dissect functional groups, propose reaction pathways, and evaluate the influence of catalysts, inhibitors, and reaction conditions.
By unraveling the complexities of draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:, we gain a profound understanding of chemical reactivity and the factors that govern molecular transformations.
As we progress, we will encounter various reaction mechanisms, each possessing its own strengths and weaknesses. Through careful analysis and experimental evidence, we will discern the most plausible mechanism for a given reaction. Furthermore, we will explore the stereochemistry of reactions, unraveling the factors that determine the formation of specific stereoisomers.
By the conclusion of this guide, you will possess a comprehensive understanding of draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: and its applications in various chemical contexts.
Reaction Mechanism
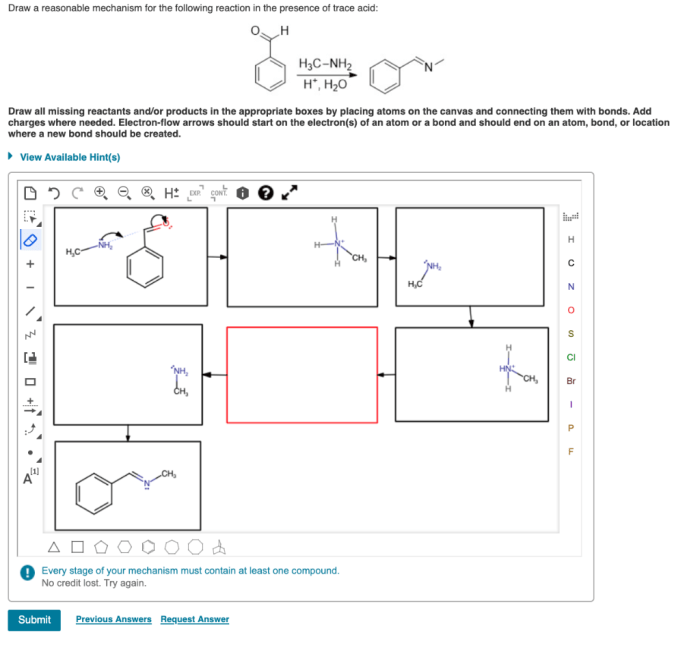
A reaction mechanism provides a detailed step-by-step description of the chemical changes that occur during a reaction. It identifies the reactive sites, intermediates, and electronic changes involved in the transformation of reactants to products.
1. Identify Functional Groups and Reactive Sites
- Functional groupsare specific arrangements of atoms within a molecule that determine its chemical properties and reactivity.
- Reactive sitesare the specific atoms or bonds within a functional group that are most likely to undergo chemical reactions.
By understanding the functional groups and reactive sites present in the reactants, we can predict the potential pathways for the reaction.
2. Propose a Reaction Mechanism
A reaction mechanism typically involves the following steps:
- Initiation:The reaction is initiated by the formation of a reactive species, such as a free radical or ion.
- Propagation:The reactive species reacts with other molecules to form new reactive species and products.
- Termination:The reaction is terminated when two reactive species combine to form a stable product.
The mechanism is illustrated using curved arrows to show the movement of electrons and the formation and breaking of bonds.
3. Consider Catalysts and Inhibitors
- Catalystsare substances that increase the rate of a reaction without being consumed.
- Inhibitorsare substances that decrease the rate of a reaction.
Understanding the role of catalysts and inhibitors is crucial for optimizing reaction conditions and controlling the selectivity of the reaction.
4. Evaluate Reaction Conditions
The optimal reaction conditions (e.g., temperature, pressure, solvent) can significantly affect the reaction rate and selectivity.
Factors to consider include:
- Temperature:Higher temperatures generally increase the reaction rate but can also lead to side reactions.
- Pressure:Increased pressure can favor reactions that involve gases.
- Solvent:The solvent can influence the solubility of the reactants and products and can also participate in the reaction.
5. Analyze Reaction Stereochemistry, Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:
For reactions that involve the formation of chiral products, the stereochemistry of the products must be determined.
Factors that influence the stereoselectivity of a reaction include:
- The stereochemistry of the reactants:The stereochemistry of the reactants can influence the stereochemistry of the products.
- The reaction mechanism:The mechanism of the reaction can determine the stereochemistry of the products.
- The presence of chiral catalysts or auxiliaries:Chiral catalysts or auxiliaries can be used to control the stereochemistry of the products.
6. Compare with Alternative Mechanisms
In some cases, there may be multiple possible mechanisms for a reaction.
Factors to consider when comparing alternative mechanisms include:
- The plausibility of the mechanism:The mechanism should be consistent with the experimental evidence and the known chemistry of the reactants.
- The energy profile of the mechanism:The mechanism should have a reasonable activation energy and should be consistent with the observed reaction rate.
- The selectivity of the mechanism:The mechanism should be consistent with the observed selectivity of the reaction.
Detailed FAQs: Draw A Reasonable Mechanism For The Following Reaction:
What is the significance of functional groups in draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:?
Functional groups are the reactive centers of molecules, and their presence and nature dictate the chemical reactivity of a molecule. By identifying the functional groups present in reactants and products, we can infer the possible reaction pathways and predict the products.
How do catalysts facilitate draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:?
Catalysts are substances that increase the reaction rate without being consumed in the reaction. They provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, allowing the reaction to proceed more rapidly at lower temperatures or with lower energy input.
What factors influence the stereochemistry of draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:?
The stereochemistry of a reaction is determined by the spatial arrangement of atoms and groups in the reactants and products. Factors such as the geometry of the reactants, the reaction mechanism, and the presence of chiral centers can influence the stereochemical outcome of a reaction.