Is baking soda a pure substance homogeneous or heterogeneous – Embark on a captivating exploration of the nature of baking soda, delving into its classification as a pure substance and examining whether it exhibits homogeneous or heterogeneous characteristics. This inquiry will shed light on the fundamental properties of matter and provide insights into the applications of this versatile substance.
Baking soda, a common household staple, holds a unique place in the realm of chemistry. Understanding its composition and properties is crucial for harnessing its potential in various fields. This comprehensive analysis will unravel the mysteries surrounding baking soda, revealing its true nature and the implications for its diverse applications.
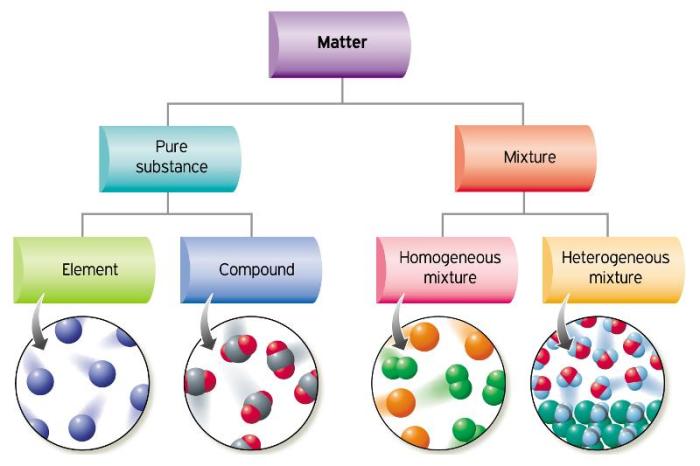
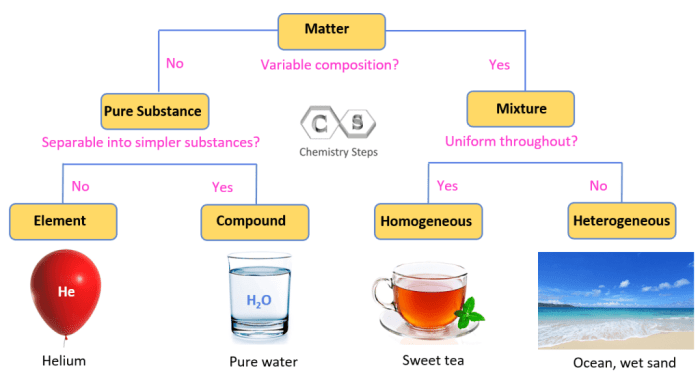
Definition of Pure Substances
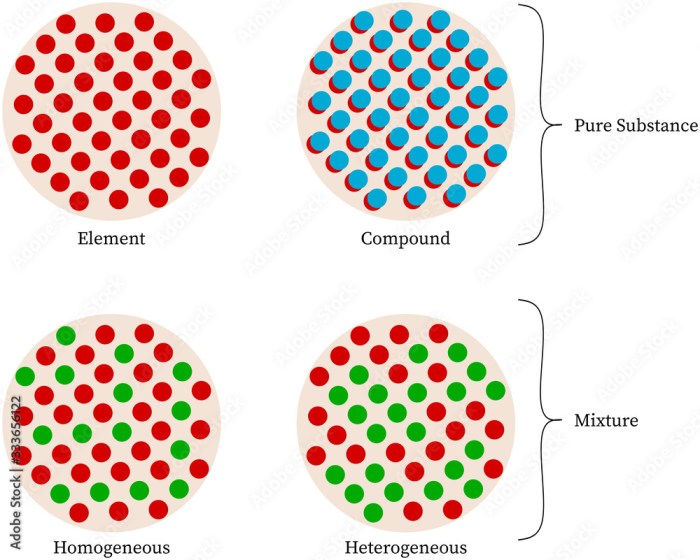
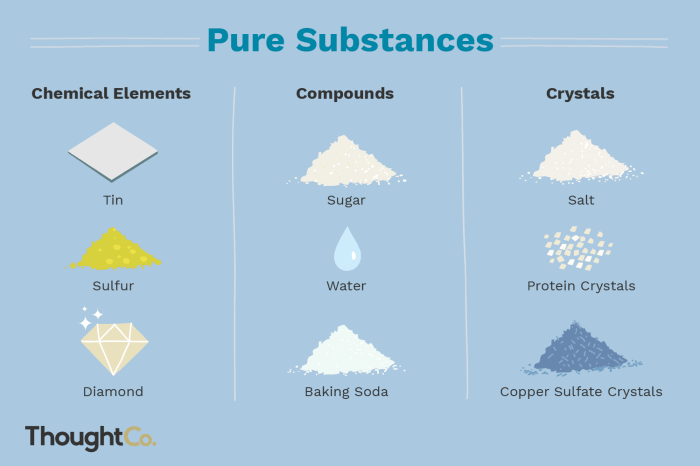
A pure substance is a substance that contains only one type of molecule. Pure substances can be either elements or compounds. Elements are the simplest type of pure substance and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
Compounds are made up of two or more elements that are chemically combined. Pure substances have a definite composition and a definite set of properties.
Types of Pure Substances
- Elements: Elements are the simplest type of pure substance and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Examples of elements include hydrogen, oxygen, and gold.
- Compounds: Compounds are made up of two or more elements that are chemically combined. Examples of compounds include water (H 2O), salt (NaCl), and sugar (C 12H 22O 11).
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures
A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. This means that the composition of the mixture is the same at any point in the mixture. Examples of homogeneous mixtures include salt water and air.
A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture. This means that the composition of the mixture can vary from one point in the mixture to another. Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include sand in water and oil in water.
Baking Soda as a Pure Substance
Baking soda is a pure substance because it contains only one type of molecule, sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO 3). Baking soda is a compound that is made up of the elements sodium, hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen.
Properties of Baking Soda
- Physical properties: Baking soda is a white, crystalline powder that is soluble in water. It has a slightly salty taste and a pH of about 8.3.
- Chemical properties: Baking soda is a base that reacts with acids to produce carbon dioxide gas. It is also a mild oxidizing agent.
Applications of Baking Soda: Is Baking Soda A Pure Substance Homogeneous Or Heterogeneous
- Baking: Baking soda is used as a leavening agent in baking. It reacts with acids in the batter or dough to produce carbon dioxide gas, which causes the batter or dough to rise.
- Cleaning: Baking soda is used as a cleaning agent because it is a mild abrasive and a deodorant. It can be used to clean surfaces, remove stains, and deodorize refrigerators.
- Personal care: Baking soda is used in personal care products such as toothpaste, deodorant, and shampoo. It can help to whiten teeth, remove bad breath, and soothe skin irritation.
FAQs
Is baking soda a compound or an element?
Baking soda is a compound composed of sodium, hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen atoms.
Why is baking soda considered a pure substance?
Baking soda meets the criteria of a pure substance as it has a definite and uniform composition throughout, consisting solely of sodium bicarbonate molecules.
How does baking soda differ from a heterogeneous mixture?
Unlike heterogeneous mixtures, which exhibit varying compositions and distinct phases, baking soda is homogeneous, meaning its composition and properties are consistent throughout.