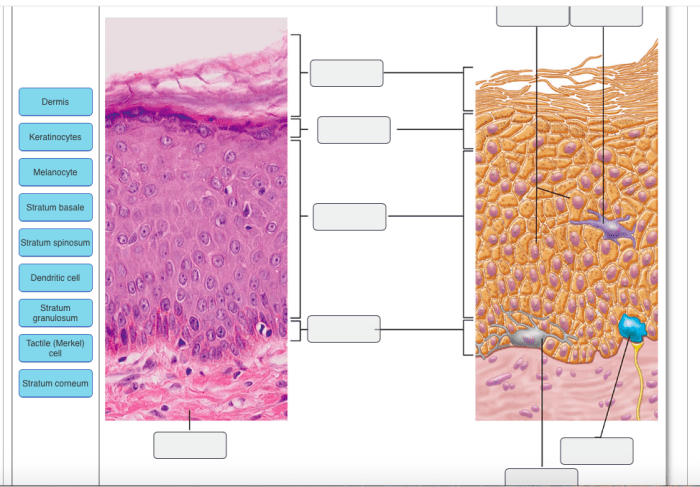
Art-labeling activity melanocyte in the stratum basale of the epidermis presents a groundbreaking technique that enables the precise identification and characterization of melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin pigmentation. This innovative approach holds immense significance in dermatological research and diagnostics, providing valuable insights into skin biology and disease processes.
Melanocytes, residing within the basal layer of the epidermis, play a crucial role in melanin production, determining skin color and providing protection against harmful UV radiation. Art-labeling, a specialized technique, employs specific antibodies to selectively bind to melanocytes, allowing for their visualization and detailed analysis.
Art-Labeling Activity: Introduction: Art-labeling Activity Melanocyte In The Stratum Basale Of The Epidermis
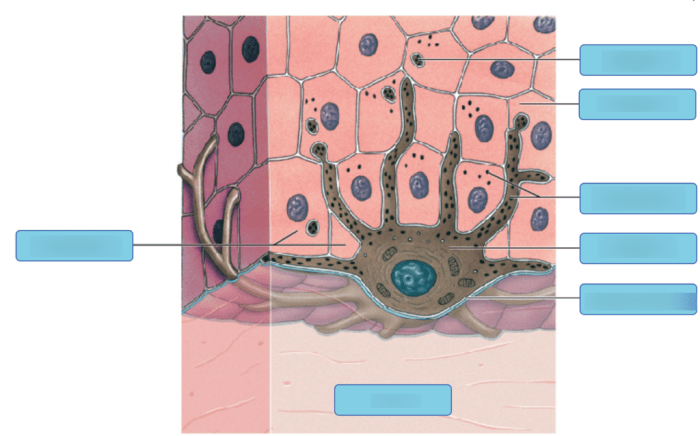
Art-labeling activities play a crucial role in dermatological research and diagnostics. They involve the specific identification and visualization of cells or structures within skin tissues, providing valuable insights into their distribution, morphology, and function.
Labeling melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells located in the stratum basale of the epidermis, is of particular significance. Melanocytes are responsible for skin pigmentation and their distribution and activity can provide valuable information in understanding various skin conditions.
Melanocytes and Their Role
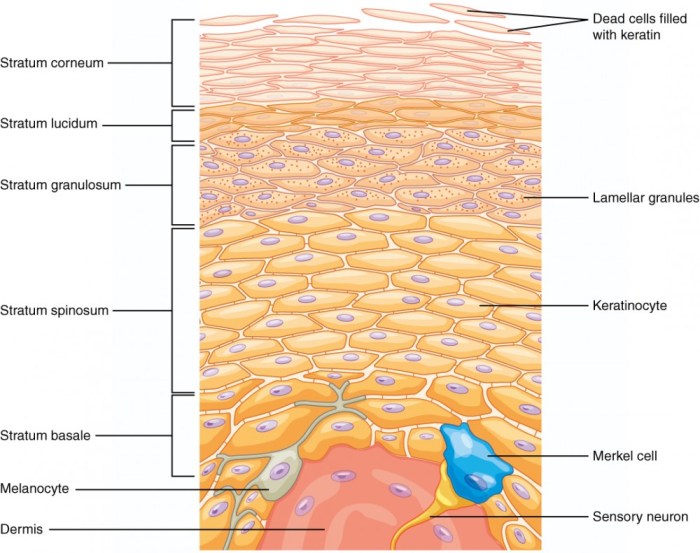
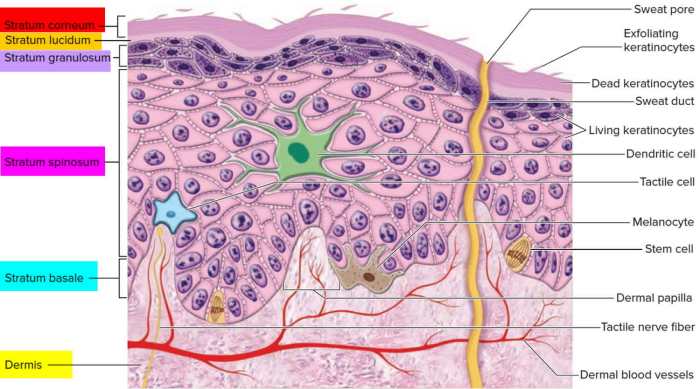
Melanocytes are specialized cells that produce melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. They are located in the basal layer of the epidermis and are responsible for synthesizing and distributing melanin to surrounding keratinocytes.
- Structure: Melanocytes have a dendritic shape, with long, branching extensions that reach out to neighboring keratinocytes.
- Function: Melanocytes produce melanin in response to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Melanin absorbs UV radiation, protecting the skin from damage.
Stratum Basale and Its Significance
The stratum basale is the innermost layer of the epidermis, directly above the basement membrane. It is composed of a single layer of cuboidal or columnar cells, including melanocytes.
- Structure: The stratum basale is characterized by tightly packed cells that are constantly dividing and renewing the epidermis.
- Function: Melanocytes in the stratum basale play a crucial role in skin pigmentation by synthesizing and distributing melanin to the overlying layers of the epidermis.
Art-Labeling Methodology, Art-labeling activity melanocyte in the stratum basale of the epidermis
Art-labeling is a technique used to specifically identify and visualize melanocytes in the stratum basale. It involves the use of antibodies that bind to specific proteins expressed by melanocytes.
- Principle: Art-labeling relies on the principle of antigen-antibody binding. Antibodies are designed to recognize and bind to specific proteins, in this case, proteins expressed by melanocytes.
- Steps: Tissue sections are incubated with the antibodies, which bind to the target proteins. The bound antibodies are then visualized using a chromogenic or fluorescent substrate.
Interpretation and Applications
The interpretation of art-labeling results involves identifying the cells that have bound to the antibodies, which represent the melanocytes in the stratum basale.
Art-labeling has various applications in dermatological research and diagnostics, including:
- Studying the distribution and density of melanocytes in different skin conditions.
- Investigating the role of melanocytes in skin pigmentation disorders, such as vitiligo and melanoma.
- Assessing the effects of UV radiation on melanocyte activity and skin pigmentation.
Examples and Case Studies
Numerous art-labeling studies have been conducted to investigate melanocytes in the stratum basale and their role in skin pigmentation.
One study, published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, used art-labeling to examine the distribution of melanocytes in vitiligo patients. The study found that melanocytes were significantly reduced in the affected areas, providing insights into the underlying mechanisms of this skin disorder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of art-labeling melanocytes in the stratum basale?
Art-labeling allows for the precise identification and characterization of melanocytes, providing valuable insights into their distribution, morphology, and function within the epidermis.
How does art-labeling aid in the study of skin pigmentation disorders?
By selectively labeling melanocytes, art-labeling enables researchers to investigate the alterations in melanocyte activity and distribution associated with various pigmentation disorders, such as vitiligo and hyperpigmentation.
What are the applications of art-labeling in melanoma research?
Art-labeling plays a crucial role in melanoma research, allowing for the early detection and characterization of atypical melanocytes, aiding in the diagnosis and prognosis of melanoma.